Medical surgical telemetry a relias, a transformative technology in healthcare, empowers medical professionals with real-time patient data, revolutionizing patient monitoring and enhancing healthcare delivery. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of telemetry systems, their components, benefits, applications, and future advancements, providing a thorough understanding of this essential technology.
Introduction to Medical-Surgical Telemetry: Medical Surgical Telemetry A Relias

Medical-surgical telemetry is a sophisticated monitoring system that wirelessly transmits real-time patient data from bedside monitors to a central monitoring station. This technology enables continuous surveillance of a patient’s vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation, allowing for prompt detection and intervention in case of any abnormalities.
Telemetry monitoring is particularly beneficial for patients with conditions that require close monitoring, such as arrhythmias, unstable vital signs, or respiratory distress. By providing continuous data, telemetry helps clinicians identify subtle changes in a patient’s condition, enabling timely interventions to prevent complications and improve patient outcomes.
Benefits of Telemetry Monitoring
- Continuous monitoring of vital signs
- Early detection of abnormalities
- Prompt intervention to prevent complications
- Improved patient safety and outcomes
Components of a Telemetry System
A telemetry system consists of various components that work together to collect, transmit, and monitor patient data wirelessly. These components include sensors, transmitters, receivers, and monitoring devices.
Sensors are placed on or within the patient’s body to detect and measure physiological parameters such as heart rate, blood pressure, and temperature. The sensors convert these measurements into electrical signals, which are then transmitted to the transmitter.
Transmitters
Transmitters are small, battery-powered devices that are attached to the patient’s body. They receive the electrical signals from the sensors and convert them into radio waves. The radio waves are then transmitted to the receiver.
Receivers
Receivers are located in the patient’s room or at a central monitoring station. They receive the radio waves from the transmitters and convert them back into electrical signals. The electrical signals are then sent to the monitoring devices.
Monitoring Devices
Monitoring devices are used to display and record the patient’s physiological data. They can be standalone devices or integrated into a hospital’s electronic health record system. Monitoring devices typically include alarms that alert caregivers to changes in the patient’s condition.
Benefits of Telemetry Monitoring
Telemetry monitoring offers numerous advantages in healthcare, including:
Improved Patient Safety
Telemetry monitoring continuously tracks vital signs, enabling early detection of physiological changes that may indicate potential complications. This allows for prompt intervention and treatment, reducing the risk of adverse events and improving patient safety.
Early Detection of Complications
By monitoring vital signs in real-time, telemetry can detect subtle changes that may not be apparent during routine assessments. This enables early identification of complications such as arrhythmias, respiratory distress, and sepsis, allowing for timely intervention and improved outcomes.
Reduced Healthcare Costs
Telemetry monitoring can reduce healthcare costs by enabling early detection and management of complications, preventing the need for more expensive interventions and hospitalizations. By identifying potential problems early on, telemetry can help prevent unnecessary tests, procedures, and extended hospital stays.
Improved Patient Outcomes
Numerous studies have demonstrated the benefits of telemetry monitoring in improving patient outcomes. For example, telemetry has been shown to reduce the incidence of cardiac arrests, improve survival rates in patients with acute coronary syndromes, and shorten hospital stays for patients with pneumonia.
Applications of Telemetry in Healthcare
Telemetry has revolutionized healthcare by enabling the remote monitoring of patients’ vital signs and physiological parameters. This technology has numerous applications across various healthcare settings, including:
Cardiac Monitoring
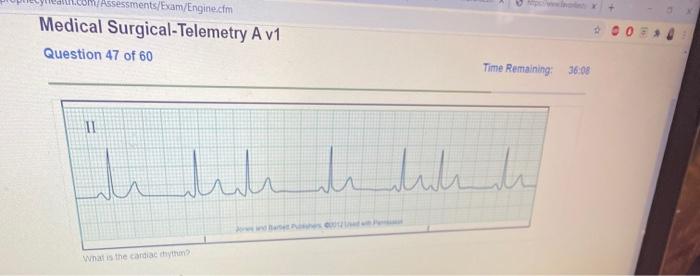
Telemetry is widely used in cardiac monitoring to detect and manage heart conditions. It allows healthcare professionals to continuously monitor a patient’s electrocardiogram (ECG), which provides real-time information about the heart’s electrical activity. This helps identify arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other cardiac events promptly, facilitating timely intervention and improving patient outcomes.
Respiratory Monitoring
Telemetry can monitor respiratory parameters such as breathing rate, oxygen saturation, and lung sounds. It enables early detection of respiratory distress, exacerbations in chronic lung diseases, and other respiratory emergencies. Telemetry-based respiratory monitoring is particularly beneficial for patients with compromised respiratory function, such as those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or sleep apnea.
Neurological Monitoring
Telemetry plays a crucial role in neurological monitoring, allowing healthcare professionals to assess brain activity and detect neurological events. It can monitor electroencephalography (EEG), which records electrical activity in the brain, helping identify seizures, strokes, and other neurological disorders. Telemetry-based neurological monitoring is essential in critical care settings, such as intensive care units (ICUs), where patients require close neurological surveillance.
Remote Patient Monitoring
Telemetry has enabled remote patient monitoring (RPM), where patients’ vital signs and physiological parameters are monitored from a distance. This allows healthcare providers to monitor patients with chronic conditions or those recovering from surgery in the comfort of their own homes.
RPM facilitates timely intervention, reduces hospital readmissions, and improves patient satisfaction.
Considerations for Implementing Telemetry
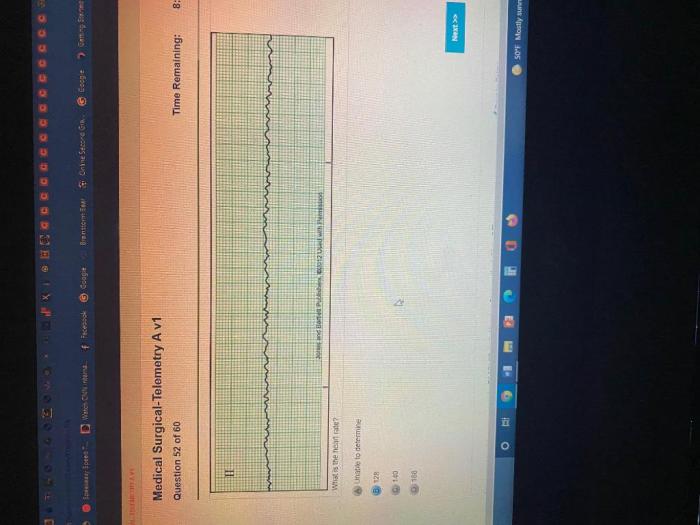
Implementing a telemetry system involves careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal patient care and effective monitoring. These factors include:
Patient Population
The patient population determines the type and level of monitoring required. For example, patients with cardiac conditions may require continuous electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring, while patients with respiratory issues may require pulse oximetry monitoring.
Monitoring Needs, Medical surgical telemetry a relias
The specific monitoring needs of the patients should be identified to select the appropriate telemetry system. This includes determining the number of parameters to be monitored, the frequency of monitoring, and the desired level of data storage and analysis.
Cost
The cost of implementing and maintaining a telemetry system should be carefully evaluated. This includes the cost of equipment, installation, maintenance, and ongoing support.
Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare organizations must comply with regulatory requirements related to telemetry monitoring. These requirements may vary depending on the location and type of healthcare facility.
Selecting and Implementing a Telemetry System
To select and implement a telemetry system that meets the specific needs of a healthcare organization, the following steps should be considered:
- Conduct a thorough assessment of the patient population and monitoring needs.
- Research and evaluate different telemetry systems based on functionality, cost, and compliance requirements.
- Develop a plan for implementation, including equipment installation, staff training, and data management protocols.
- Implement the telemetry system and monitor its performance to ensure optimal patient care and data accuracy.
Future of Telemetry in Healthcare
The future of telemetry in healthcare holds immense potential for revolutionizing patient monitoring and healthcare delivery. Emerging trends and advancements in telemetry technology, such as wearable sensors, wireless monitoring, and artificial intelligence (AI), are poised to transform the way healthcare providers monitor and manage patient health.
Wearable Sensors
Wearable sensors are becoming increasingly popular for continuous monitoring of vital parameters, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and activity levels. These sensors are small, comfortable, and can be worn on the body for extended periods. By continuously collecting data, wearable sensors provide a more comprehensive and real-time view of a patient’s health status, enabling early detection of potential health issues and timely interventions.
Wireless Monitoring
Wireless monitoring systems eliminate the need for cumbersome wires and cables, allowing patients to move freely while being monitored. This enhances patient comfort and mobility, promoting a more natural and less restrictive monitoring experience. Wireless monitoring systems also enable remote monitoring, allowing healthcare providers to monitor patients from afar, facilitating timely interventions and reducing the need for hospital stays.
Artificial Intelligence
AI is playing a significant role in enhancing the capabilities of telemetry systems. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data collected from telemetry devices, identifying patterns and trends that may not be apparent to human observers. This enables more accurate and timely detection of health issues, personalized treatment plans, and predictive analytics to anticipate potential health risks and prevent adverse events.
Key Questions Answered
What are the key components of a telemetry system?
Telemetry systems comprise sensors, transmitters, receivers, and monitoring devices that work together to collect, transmit, and display patient data.
How does telemetry monitoring benefit patient care?
Telemetry monitoring enhances patient safety, enables early detection of complications, reduces healthcare costs, and improves overall patient outcomes.
What are the applications of telemetry in healthcare?
Telemetry finds applications in cardiac monitoring, respiratory monitoring, neurological monitoring, and remote patient monitoring.
What factors should be considered when implementing a telemetry system?
Patient population, monitoring needs, cost, and regulatory compliance are key factors to consider when implementing a telemetry system.
What advancements are shaping the future of telemetry in healthcare?
Wearable sensors, wireless monitoring, and artificial intelligence are emerging trends that hold the potential to revolutionize patient monitoring and healthcare delivery.