Nursing care cystic fibrosis edapt – Nursing care for cystic fibrosis has evolved significantly with the introduction of EDAPT therapy, a groundbreaking treatment that offers promising outcomes for patients. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of nursing care for cystic fibrosis, exploring the role of nurses, the principles of care, and the transformative impact of EDAPT therapy.
EDAPT therapy, an acronym for Electrical Discharge Airway Pressure Therapy, represents a paradigm shift in the management of cystic fibrosis. By utilizing high-voltage electrical pulses, this innovative therapy targets the underlying pathophysiology of the disease, offering hope for improved lung function and reduced exacerbations.
Cystic Fibrosis Overview
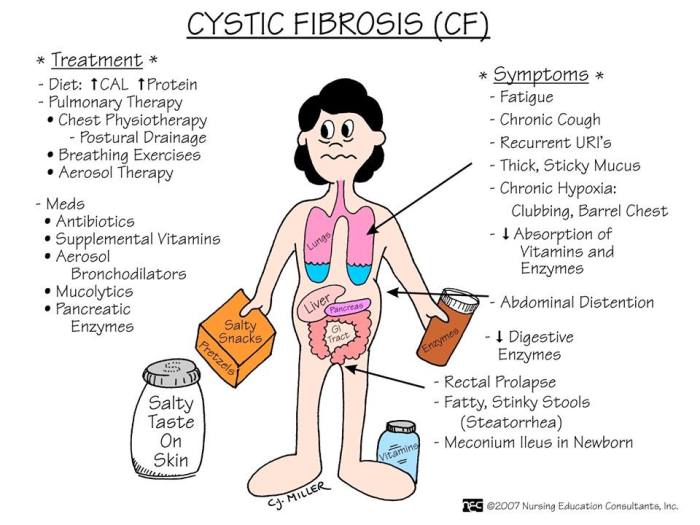
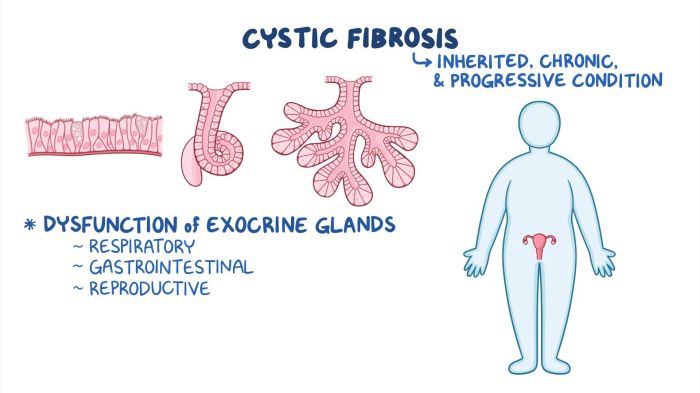
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder that affects the lungs, digestive system, and other organs. It is caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, which leads to the production of thick, sticky mucus that can clog the airways and digestive tract.
CF is a relatively common condition, affecting approximately 1 in 3,000 newborns in the United States. It is more common in people of European descent and is less common in people of African or Asian descent.
The history of CF research and treatment dates back to the early 1900s. In 1938, Dorothy Andersen described the condition as “cystic fibrosis of the pancreas” and recognized its fatal nature. In the 1950s, the sweat test was developed as a way to diagnose CF, and in the 1980s, the CFTR gene was identified.
Nursing Care for Cystic Fibrosis
Nurses play a vital role in the management of CF. They provide education and support to patients and their families, and they work with other members of the healthcare team to develop and implement treatment plans.
The principles of nursing care for CF patients include:
- Promoting airway clearance
- Preventing and treating infections
- Managing nutritional needs
- Providing psychosocial support
Nursing care for CF patients can be challenging, but it is also rewarding. Nurses who work with CF patients have the opportunity to make a real difference in their lives.
EDAPT Therapy for Cystic Fibrosis: Nursing Care Cystic Fibrosis Edapt
EDAPT therapy is a non-invasive treatment for CF that uses electrical pulses to thin and loosen mucus in the airways. This can help to improve lung function and reduce the risk of exacerbations.
The mechanism of action of EDAPT therapy is not fully understood, but it is thought to work by stimulating the production of nitric oxide in the airways. Nitric oxide is a gas that helps to relax the airways and thin mucus.
Clinical evidence supporting the use of EDAPT therapy for CF includes a number of studies that have shown that the therapy can improve lung function and reduce the risk of exacerbations.
The EDAPT therapy procedure is relatively simple. The patient sits in a chair and wears a vest that delivers electrical pulses to the chest. The treatment lasts for about 30 minutes and is typically repeated once or twice a day.
Benefits of EDAPT Therapy for Cystic Fibrosis
EDAPT therapy has been shown to be effective in improving lung function in CF patients. In one study, patients who received EDAPT therapy had a significant improvement in their FEV1 (forced expiratory volume in 1 second) compared to patients who received placebo.
EDAPT therapy has also been shown to reduce the risk of exacerbations in CF patients. In one study, patients who received EDAPT therapy had a 50% reduction in the risk of exacerbations compared to patients who received placebo.
EDAPT therapy is generally well-tolerated, with few side effects. The most common side effects are mild and include skin irritation and headache.
Challenges and Limitations of EDAPT Therapy
EDAPT therapy is not a cure for CF, and it does not work for all patients. Some patients may not experience any benefit from the therapy, and others may experience side effects that make the therapy intolerable.
EDAPT therapy is also relatively expensive, and it is not covered by all insurance plans. This can make it difficult for some patients to access the therapy.
Despite these challenges, EDAPT therapy is a promising treatment for CF. It has been shown to improve lung function and reduce the risk of exacerbations, and it is generally well-tolerated. Further research is needed to determine the long-term benefits of EDAPT therapy and to identify the patients who are most likely to benefit from the therapy.
Quick FAQs
What is the role of nurses in managing cystic fibrosis?
Nurses play a pivotal role in providing comprehensive care for cystic fibrosis patients, including monitoring symptoms, administering treatments, and educating patients and their families about the condition.
How does EDAPT therapy work?
EDAPT therapy uses high-voltage electrical pulses to create an electrical field within the lungs, which helps to thin mucus and improve airflow.
What are the benefits of EDAPT therapy for cystic fibrosis?
EDAPT therapy has been shown to improve lung function, reduce exacerbations and hospitalizations, and enhance overall quality of life for cystic fibrosis patients.