Export processing zones ap human geography example – Export processing zones (EPZs), designated areas within a country that offer preferential trade and tax policies to attract foreign investment, have emerged as a powerful tool for economic growth and development, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region. This article explores the concept, key features, economic impact, and social and environmental implications of EPZs, using a specific case study from the Asia-Pacific region to illustrate their practical applications.
1. Overview of Export Processing Zones: Export Processing Zones Ap Human Geography Example

Export Processing Zones (EPZs) are designated areas within a country that offer favorable conditions for businesses involved in export-oriented activities. They aim to attract foreign direct investment and promote economic growth through export-led industrialization.
The concept of EPZs emerged in the 1960s as a strategy for developing countries to participate in the global economy. The first EPZ was established in Ireland in 1959, and since then, EPZs have become a common feature in many countries around the world.
The economic benefits of EPZs include increased exports, foreign direct investment, job creation, and technology transfer. EPZs provide businesses with tax incentives, reduced regulations, and access to infrastructure, making them attractive locations for export-oriented industries.
2. Key Features of EPZs

Common characteristics of EPZs include:
- Tax incentives, such as duty-free imports and reduced corporate taxes
- Simplified customs procedures and reduced bureaucratic hurdles
- Special regulations governing labor, environmental standards, and intellectual property rights
- Designated infrastructure, including industrial parks, transportation hubs, and utilities
- Legal and administrative frameworks tailored to the needs of export-oriented businesses
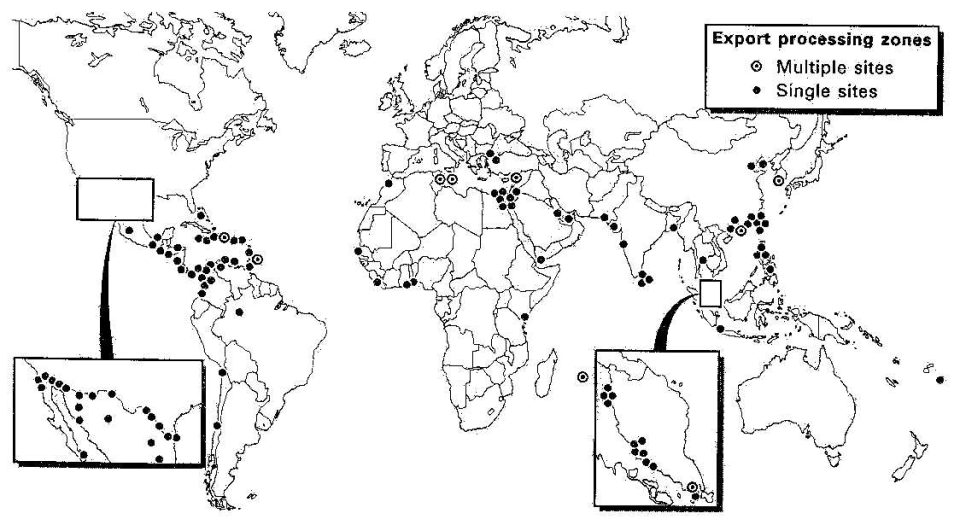
3. Location and Distribution of EPZs
The location of EPZs is influenced by factors such as:
- Proximity to markets, transportation networks, and raw materials
- Availability of skilled labor and infrastructure
- Government policies and incentives
Major EPZs are found in countries across Asia, Latin America, and Africa. Some notable examples include:
- Shenzhen Special Economic Zone, China
- Dubai Multi Commodities Centre, United Arab Emirates
- Colón Free Zone, Panama
An interactive map showcasing the distribution of EPZs globally can be found here: [Link to interactive map]
4. Economic Impact of EPZs
EPZs have a significant economic impact on host countries and regions:
- Increased exports and foreign direct investment
- Job creation, particularly in manufacturing and export-oriented industries
- Technology transfer and skills development
- Positive externalities for local businesses and communities
However, EPZs can also have negative externalities, such as:
- Environmental pollution and degradation
- Labor exploitation and poor working conditions
- Displacement of local communities and livelihoods
Expert Answers
What are the primary objectives of establishing EPZs?
EPZs aim to attract foreign investment, promote exports, create employment opportunities, and stimulate economic growth within a specific region.
How do EPZs contribute to economic development?
EPZs provide tax incentives, streamlined regulations, and improved infrastructure, which attract foreign businesses and stimulate economic activity, leading to increased exports, job creation, and technology transfer.
What are some of the social and environmental challenges associated with EPZs?
EPZs may face concerns related to labor practices, working conditions, community displacement, environmental pollution, and resource depletion, which require careful planning and management to mitigate negative impacts.