Select the true statements about denaturation – The concept of protein denaturation, a phenomenon that unfolds when the delicate structure of proteins unravels, takes center stage in this discourse. As we delve into the intricacies of denaturation, we will explore its causes, consequences, and practical applications, shedding light on a process that profoundly impacts the world of proteins.
Delving deeper, we will uncover the various factors that can trigger denaturation, including the influence of temperature, pH, and solvents. We will also examine the impact of denaturation on protein function and stability, unraveling the relationship between denaturation and protein aggregation.
Definition of Denaturation
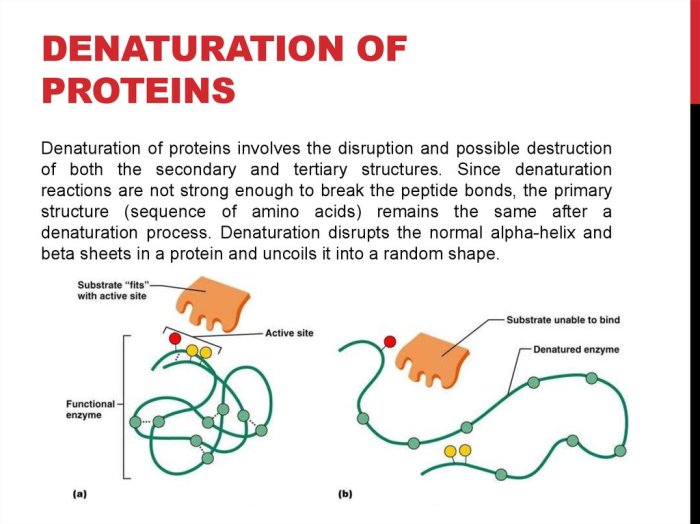
Denaturation is a process that causes the alteration of a protein’s native structure, leading to the loss of its biological function. It involves the disruption of non-covalent bonds, such as hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and disulfide bonds, that maintain the protein’s tertiary and quaternary structures.
Causes of Denaturation

Temperature, Select the true statements about denaturation
Extreme temperatures, both high and low, can cause protein denaturation. High temperatures disrupt hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions, while low temperatures can lead to protein aggregation.
pH
Changes in pH can also denature proteins. Extreme pH values can disrupt ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds, altering the protein’s structure and charge.
Solvents
Organic solvents, such as alcohol and acetone, can denature proteins by disrupting hydrophobic interactions. They can also interact with the protein’s side chains, altering its conformation.
Consequences of Denaturation
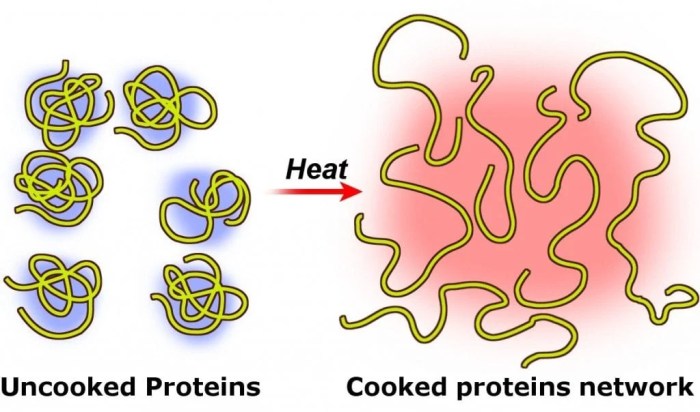
Loss of Function
Denaturation typically leads to the loss of protein function. The altered structure of the protein disrupts its active site, preventing it from binding to ligands or carrying out its catalytic activity.
Protein Aggregation
Denatured proteins can aggregate with each other, forming insoluble clumps. This aggregation can further impair protein function and lead to cellular toxicity.
Applications of Denaturation

Food Processing
Denaturation is used in food processing to improve the texture, flavor, and shelf life of food products. For example, heat treatment of milk denatures whey proteins, resulting in the formation of a gel that gives yogurt its characteristic texture.
Biotechnology
Denaturation is also used in biotechnology for protein purification and characterization. Controlled denaturation can help separate proteins based on their stability and solubility.
Frequently Asked Questions: Select The True Statements About Denaturation
What is protein denaturation?
Protein denaturation refers to the process by which the intricate structure of a protein unravels, leading to a loss of its native conformation and biological activity.
What causes protein denaturation?
Denaturation can be triggered by various factors, including exposure to extreme temperatures, pH changes, exposure to solvents, and mechanical stress.
What are the consequences of protein denaturation?
Denaturation can impair protein function, reduce its solubility, and increase its susceptibility to aggregation, potentially leading to loss of biological activity.