Embark on an enlightening journey with our comprehensive waves and the electromagnetic spectrum worksheet, designed to unravel the captivating world of waves and their profound impact on our universe. Delve into the depths of this multifaceted topic, where the symphony of waves orchestrates a harmonious dance of energy and information.
From the ethereal embrace of radio waves to the enigmatic power of gamma rays, this worksheet unveils the captivating tapestry of the electromagnetic spectrum, unraveling the unique characteristics and applications of each wave type. Prepare to be captivated as we navigate the intricate interplay between frequency, wavelength, and energy, deciphering the secrets that govern the behavior of these enigmatic entities.
1. Introduction: Waves And The Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet
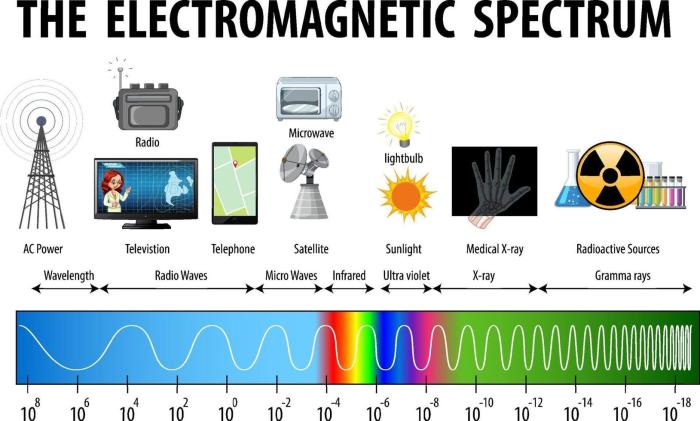
Waves are a fundamental part of our universe and play a crucial role in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are characterized by their oscillatory motion, transferring energy through space and time. The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a wide range of waves, each with distinct properties and applications.
2. Types of Waves
Radio Waves
Radio waves have the lowest frequency and longest wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are used for communication, navigation, and remote control devices.
Microwaves
Microwaves have higher frequencies and shorter wavelengths than radio waves. They are commonly used in microwave ovens, radar systems, and satellite communications.
Infrared Radiation
Infrared radiation has even higher frequencies and shorter wavelengths than microwaves. It is emitted by warm objects and used in applications such as night vision, heat detection, and remote sensing.
Visible Light, Waves and the electromagnetic spectrum worksheet
Visible light is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be detected by the human eye. It consists of a range of colors, from red (lowest frequency) to violet (highest frequency).
Ultraviolet Radiation
Ultraviolet radiation has higher frequencies and shorter wavelengths than visible light. It is used in tanning beds, water purification, and medical diagnostics.
X-rays
X-rays have even higher frequencies and shorter wavelengths than ultraviolet radiation. They are used in medical imaging, security screening, and crystallography.
Gamma Rays
Gamma rays have the highest frequencies and shortest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are emitted by radioactive materials and used in cancer treatment and medical imaging.
| Type of Wave | Frequency Range | Wavelength Range | Energy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radio Waves | 3 Hz
|
100 km
|
Low |
| Microwaves | 300 MHz
|
1 m
|
Medium |
| Infrared Radiation | 300 GHz
|
1 mm
|
High |
| Visible Light | 400 THz
|
700 nm
|
Higher |
| Ultraviolet Radiation | 790 THz
|
400 nm
|
Very High |
| X-rays | 30 PHz
|
10 nm
|
Extremely High |
| Gamma Rays | >30 EHz | <0.01 nm | Highest |
3. Applications of Waves
Communication
Radio waves, microwaves, and infrared radiation are used in various communication systems, including cell phones, Wi-Fi, and satellite communications.
Medicine
X-rays, gamma rays, and infrared radiation are used in medical imaging, diagnosis, and treatment. Microwaves are used in microwave ablation, a minimally invasive surgical technique.
Scientific Research
Visible light, ultraviolet radiation, and X-rays are used in spectroscopy, microscopy, and crystallography. Radio waves and microwaves are used in astronomy and remote sensing.
4. Safety Considerations
Exposure to high levels of electromagnetic radiation can be harmful to human health. Safety measures include limiting exposure time, using shielding materials, and following recommended safety guidelines for devices that emit electromagnetic waves.
Clarifying Questions
What is the fundamental nature of waves?
Waves are disturbances that propagate energy or information through a medium or space, exhibiting oscillatory or vibratory motion.
How do different types of waves vary within the electromagnetic spectrum?
Waves in the electromagnetic spectrum differ significantly in terms of frequency, wavelength, and energy. Radio waves possess the lowest frequency and longest wavelength, while gamma rays exhibit the highest frequency and shortest wavelength.
Can you provide examples of practical applications for different wave types?
Radio waves facilitate wireless communication, microwaves power ovens, infrared radiation finds use in remote controls, visible light enables vision, ultraviolet radiation aids in disinfection, X-rays assist in medical imaging, and gamma rays contribute to cancer treatment.
What safety precautions should be taken when dealing with certain types of waves?
Exposure to high-energy waves, such as X-rays and gamma rays, requires appropriate shielding and protective measures to minimize potential health risks.